The Great American Wage Stagnation: Why Your Paycheck Isn’t Keeping Up
Related Articles
- The US Debt Ceiling: A Game Of Chicken With Global Consequences
- Navigating The Choppy Waters: A Deep Dive Into Global Supply Chain Disruptions
- Is The US Heading For A Recession? Understanding The Current Economic Landscape
- Navigating The Economic Waters: A Look At The US Forecast
- The Fed’s Balancing Act: Understanding Rate Hikes And Their Impact
Introduction
Discover everything you need to know about The Great American Wage Stagnation: Why Your Paycheck Isn’t Keeping Up
The Great American Wage Stagnation: Why Your Paycheck Isn’t Keeping Up
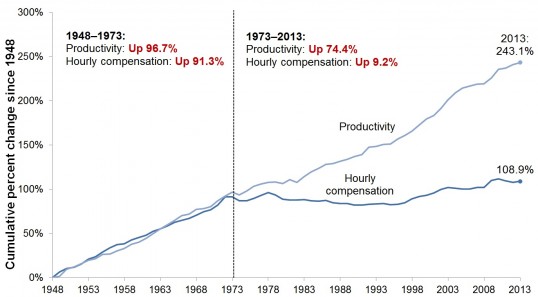
The American Dream – a life of prosperity, opportunity, and upward mobility – has always been tied to the promise of a good job that pays a decent wage. But in recent decades, that dream has become increasingly elusive for many Americans. The reality is, wages haven’t kept pace with the cost of living, leaving millions struggling to make ends meet. This phenomenon, known as wage stagnation, has become a defining issue in the American economy, impacting everything from individual financial security to the overall health of the nation.
Understanding the Roots of Wage Stagnation:
Wage stagnation is a complex issue with roots in various factors, some of which are interconnected:
- Declining Unionization: Unions have historically played a crucial role in negotiating better wages and benefits for workers. However, union membership has declined significantly since the 1980s, weakening the bargaining power of workers and contributing to wage stagnation.
- Globalization and Trade: The rise of globalization and international trade has led to increased competition from low-wage countries, putting downward pressure on wages in certain sectors. While globalization has brought benefits in terms of lower prices for consumers, it has also resulted in job displacement and wage suppression for some workers.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements have undoubtedly increased productivity and efficiency, but they have also led to job displacement in some sectors. While new jobs are often created in the tech sector, they often require higher levels of education and skills, leaving many workers behind.
- The Rise of the Gig Economy: The rise of the gig economy, with its prevalence of contract workers and independent contractors, has contributed to wage stagnation by undermining traditional employment models and reducing worker protections.
- The Decline of Manufacturing: The decline of manufacturing in the US, driven by factors like globalization and automation, has had a significant impact on wages. Manufacturing jobs historically offered higher wages and benefits, and their decline has contributed to a widening gap between the wages of skilled and unskilled workers.
- Policy Choices: Government policies, such as tax cuts for the wealthy and deregulation of the financial sector, have also contributed to wage stagnation by favoring corporations and the wealthy over workers.
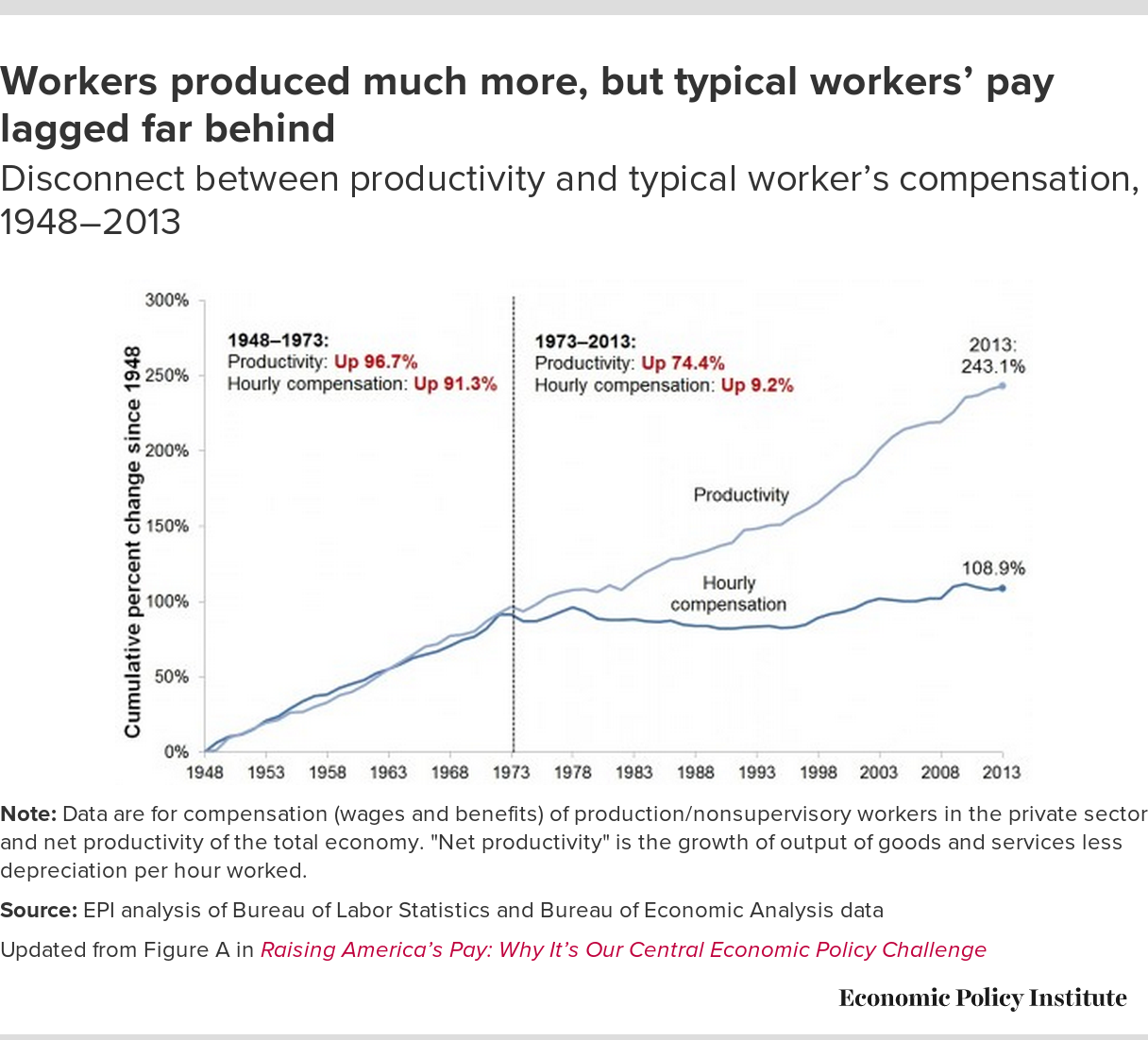
The Impact of Wage Stagnation:
The consequences of wage stagnation are far-reaching, affecting individuals, families, and the broader economy:
- Financial Strain and Inequality: Wage stagnation has led to increased financial strain for many Americans, particularly those in low-wage jobs. This has contributed to a widening gap between the rich and the poor and increased poverty rates.
- Reduced Consumer Spending: Stagnant wages mean less disposable income for consumers, leading to reduced spending and a slowdown in economic growth.
- Weakening of the Middle Class: Wage stagnation has eroded the economic security of the middle class, making it harder for families to afford basic necessities like housing, healthcare, and education.
- Political Polarization: Wage stagnation has fueled political polarization, as workers feel increasingly disenfranchised and frustrated with the current economic system.
What Can Be Done to Address Wage Stagnation?
There is no single solution to wage stagnation, but a multi-pronged approach is necessary:
- Strengthening Unions: Supporting unionization efforts and strengthening collective bargaining rights can give workers a stronger voice in negotiating wages and benefits.
- Investing in Education and Training: Investing in education and training programs can help workers acquire the skills needed for in-demand jobs in the 21st century.
- Raising the Minimum Wage: Raising the federal minimum wage to a living wage would provide a floor for wages and help lift millions of workers out of poverty.
- Promoting Fair Trade: Promoting fair trade practices that protect workers’ rights and ensure decent wages in global supply chains can help level the playing field for American workers.
- Investing in Infrastructure: Investing in infrastructure projects can create jobs and stimulate economic growth, leading to higher wages for workers.
- Tax Reform: Tax reforms that redistribute income more equitably and provide incentives for businesses to invest in workers can help address wage stagnation.
The Road Ahead:
Addressing wage stagnation is essential for the long-term health of the American economy and the well-being of its citizens. It requires a commitment from policymakers, businesses, and workers to address the root causes of the problem and implement solutions that promote economic fairness and opportunity for all.
FAQ:
Q: Is wage stagnation a new phenomenon?
A: While wage stagnation has become particularly acute in recent decades, it’s not entirely a new phenomenon. The issue has been present in various forms throughout history, often linked to economic cycles and technological advancements.
Q: Does wage stagnation affect all workers equally?
A: No, wage stagnation affects different groups of workers differently. Low-wage workers, particularly those in service sectors, have experienced the most significant wage stagnation. Workers in highly skilled professions have generally fared better, but they too have seen their wages grow at a slower pace than in previous decades.
Q: Is technology the main cause of wage stagnation?
A: While technology plays a role, it’s not the sole culprit. Factors like globalization, declining unionization, and government policies have all contributed to the problem.
Q: What is the difference between wage stagnation and income inequality?
A: Wage stagnation refers to the slow growth or decline of wages over time, while income inequality refers to the widening gap between the incomes of the rich and the poor. While wage stagnation contributes to income inequality, they are not the same thing.
Q: Can wage stagnation be reversed?
A: Yes, wage stagnation can be reversed through a combination of policy changes, economic reforms, and changes in corporate behavior. However, it requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders to address the underlying causes of the problem.
References:
- The Economic Policy Institute
- Center on Budget and Policy Priorities
- The Bureau of Labor Statistics
- The International Labour Organization
Closure
Thank you for reading! Stay with us for more insights on The Great American Wage Stagnation: Why Your Paycheck Isn’t Keeping Up.
Don’t forget to check back for the latest news and updates on The Great American Wage Stagnation: Why Your Paycheck Isn’t Keeping Up!
Feel free to share your experience with The Great American Wage Stagnation: Why Your Paycheck Isn’t Keeping Up in the comment section.
Keep visiting our website for the latest trends and reviews.