The Rollercoaster Ride of US Unemployment: A Look at the Trends and What They Mean
Related Articles
- Navigating The Inflation Maze: What’s In Store For US Consumers In 2024?
- The Economic Downturn: Navigating The Choppy Waters
- Navigating The Economic Waters: A Look At The US Forecast
- Is The US Heading For A Recession? Understanding The Current Economic Landscape
- Riding The Rollercoaster: Understanding The Impact Of Rising Interest Rates
Introduction
In this article, we dive into The Rollercoaster Ride of US Unemployment: A Look at the Trends and What They Mean, giving you a full overview of what’s to come
The Rollercoaster Ride of US Unemployment: A Look at the Trends and What They Mean
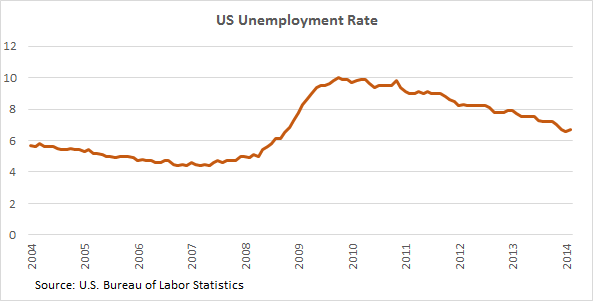
The unemployment rate, that seemingly simple number, holds a lot of weight. It’s a barometer of the nation’s economic health, reflecting the struggles of individuals and the overall state of the job market. In the United States, the unemployment rate has seen its share of ups and downs, mirroring the ebbs and flows of the economy. Let’s dive into the trends, understand the forces at play, and explore what these figures tell us about the American workforce.
A Historical Perspective: The Ups and Downs of Unemployment
To understand the present, it’s crucial to look at the past. The US unemployment rate has fluctuated significantly throughout history, influenced by a complex interplay of economic, social, and political factors.
-
The Great Depression (1929-1939): This period saw a staggering rise in unemployment, reaching a peak of 25% in 1933. The Great Depression’s legacy continues to shape economic policies and anxieties today.
-
Post-World War II Boom (1945-1973): The years following World War II witnessed a period of unprecedented economic growth and low unemployment. This era is often referred to as the "Golden Age" of American capitalism.
-
The 1970s and 1980s: This period saw a rise in inflation and stagflation, leading to increased unemployment. The oil crisis of the 1970s and the recession of the early 1980s further exacerbated the situation.
-
The 1990s and 2000s: The 1990s were a period of relative stability and low unemployment, fueled by the rise of the tech industry. However, the dot-com bubble burst in the early 2000s, leading to a recession and a spike in unemployment.
-
The Great Recession (2007-2009): The housing market crash and the subsequent financial crisis triggered a severe recession, pushing unemployment to a peak of 10% in 2009.
-
The Post-Recession Recovery (2010-2019): The economy gradually recovered from the Great Recession, with unemployment rates steadily decreasing. However, income inequality and wage stagnation remained significant concerns.
-
The COVID-19 Pandemic (2020-present): The pandemic caused a sharp rise in unemployment, reaching a peak of 14.7% in April 2020. The subsequent economic recovery has been uneven, with some sectors recovering faster than others.

Key Factors Influencing Unemployment Trends
The unemployment rate is a dynamic indicator, influenced by a multitude of factors. Here are some of the key drivers:
-
Economic Cycles: The business cycle, with its phases of expansion and contraction, plays a significant role in unemployment fluctuations. During economic booms, businesses hire more workers, leading to lower unemployment. Recessions, on the other hand, result in job losses and higher unemployment.
-
Technological Advancements: Technological innovations can create new jobs while also leading to job displacement. Automation, for instance, can reduce the need for certain types of manual labor, potentially leading to unemployment in those sectors.
-
Government Policies: Fiscal and monetary policies implemented by the government can significantly impact unemployment. Tax cuts, increased government spending, and lower interest rates can stimulate economic growth and reduce unemployment.
-
Demographics: Population growth, age distribution, and labor force participation rates all influence the unemployment rate. An aging population, for example, can lead to a decline in the labor force participation rate, impacting unemployment figures.
-
Global Economic Conditions: The US economy is deeply intertwined with the global economy. International trade, foreign investment, and global events like pandemics can all influence domestic unemployment.
Understanding the Unemployment Rate: Beyond the Numbers
While the unemployment rate provides a snapshot of the job market, it’s essential to remember that it doesn’t tell the whole story. Here are some things to keep in mind:
-
Underemployment: The unemployment rate doesn’t capture underemployment, which refers to individuals working part-time or in jobs below their skill level.
-
Discouraged Workers: The unemployment rate also excludes discouraged workers, those who have stopped actively looking for work due to a lack of opportunities.
-
Long-Term Unemployment: The unemployment rate doesn’t differentiate between short-term and long-term unemployment, which can have a significant impact on individuals and the economy.
What the Future Holds: Challenges and Opportunities
The future of the US unemployment rate is uncertain, with a complex interplay of factors shaping the job market. Some of the key challenges include:
-
Automation and Artificial Intelligence: The increasing adoption of automation and AI is likely to continue disrupting the labor market, leading to job displacement in certain sectors.
-
Globalization and Trade: The rise of global trade and competition can impact domestic job markets, leading to job losses in certain industries.
-
Income Inequality and Wage Stagnation: Persistent income inequality and wage stagnation can hinder economic growth and contribute to higher unemployment.
-
Climate Change: The impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events and resource scarcity, could disrupt industries and lead to job losses.
However, there are also opportunities for job creation:
-
Emerging Technologies: New technologies, such as renewable energy, biotechnology, and artificial intelligence, have the potential to create new jobs and industries.
-
Education and Skills Development: Investing in education and skills development can help workers adapt to the changing job market and prepare for new opportunities.
-
Entrepreneurship and Innovation: Fostering an environment that supports entrepreneurship and innovation can drive economic growth and job creation.
FAQs about US Unemployment
1. What is the current unemployment rate in the US?
The current unemployment rate in the US is [insert current rate]. This information is readily available on reputable sources like the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
2. How is the unemployment rate calculated?
The unemployment rate is calculated as the number of unemployed individuals divided by the total labor force (employed and unemployed individuals).
3. What are the different types of unemployment?
There are various types of unemployment, including:
-
Frictional unemployment: This occurs when individuals are transitioning between jobs or entering the workforce for the first time.
-
Structural unemployment: This arises due to a mismatch between the skills of workers and the requirements of available jobs.
-
Cyclical unemployment: This is associated with the business cycle, rising during recessions and falling during economic expansions.
4. What are the consequences of high unemployment?
High unemployment can have several negative consequences, including:
-
Reduced economic output: Fewer people working means less production and economic growth.
-
Increased poverty and inequality: Unemployment can lead to financial hardship and exacerbate existing inequalities.
-
Social unrest and political instability: High unemployment can contribute to social unrest and political instability.
5. What are the government’s tools for addressing unemployment?
The government uses a variety of tools to address unemployment, including:
-
Fiscal policy: This involves government spending and taxation to stimulate economic growth and create jobs.
-
Monetary policy: This involves adjusting interest rates and the money supply to influence economic activity and employment.
-
Job training programs: Government-funded programs can provide training and skills development to help unemployed individuals find new jobs.
6. What can individuals do to prepare for a changing job market?
Individuals can take several steps to prepare for a changing job market, including:
-
Investing in education and skills development: Staying up-to-date on new skills and technologies is crucial.
-
Networking and building relationships: Networking with professionals in your field can help you learn about new opportunities.
-
Developing adaptability and flexibility: Being able to adapt to new situations and learn new skills is essential for success in a changing job market.
7. What is the role of technology in the future of work?
Technology is likely to continue to play a significant role in the future of work. While automation and AI may lead to job displacement in some sectors, they also have the potential to create new jobs and industries.
8. What are the challenges and opportunities for the US labor market in the future?
The US labor market faces challenges such as automation, globalization, income inequality, and climate change. However, opportunities exist in emerging technologies, education and skills development, and entrepreneurship.
Conclusion
The unemployment rate is a complex and dynamic indicator that reflects the health of the US economy. Understanding the trends, the factors influencing them, and the challenges and opportunities facing the job market is crucial for individuals, businesses, and policymakers alike. By staying informed and proactively adapting to change, we can navigate the future of work and create a more prosperous and equitable economy for all.
Source:
- Bureau of Labor Statistics: https://www.bls.gov/
- Congressional Budget Office: https://www.cbo.gov/
- Economic Policy Institute: https://www.epi.org/
- Center on Budget and Policy Priorities: https://www.cbpp.org/
- The Brookings Institution: https://www.brookings.edu/
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the US unemployment rate trends, offering insights into the historical context, influencing factors, and future implications. By exploring the dynamics of the job market, we can gain a deeper understanding of the economic landscape and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Closure
We hope this article has helped you understand everything about The Rollercoaster Ride of US Unemployment: A Look at the Trends and What They Mean. Stay tuned for more updates!
Don’t forget to check back for the latest news and updates on The Rollercoaster Ride of US Unemployment: A Look at the Trends and What They Mean!
Feel free to share your experience with The Rollercoaster Ride of US Unemployment: A Look at the Trends and What They Mean in the comment section.
Keep visiting our website for the latest trends and reviews.