The Digital Transformation of Manufacturing: How Telecom is Revolutionizing the Industry
Related Article
- The Global Economy: A Slowdown On The Horizon?
- Feeling The Pinch: The Rising Cost Of Living In The US
- Navigating The Hybrid Insurance Maze: Everything You Need To Know
- Tax Reform And Economic Growth: A Balancing Act
- The Big Shift: How Technology Is Disrupting The Auto Insurance Market
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s uncover the essential aspects of The Digital Transformation of Manufacturing: How Telecom is Revolutionizing the Industry and why it’s relevant to you. Our aim is to provide you with fresh insights and valuable knowledge about this intriguing topic. Let’s begin and discover what The Digital Transformation of Manufacturing: How Telecom is Revolutionizing the Industry has to offer!
The Digital Transformation of Manufacturing: How Telecom is Revolutionizing the Industry

The manufacturing sector, once known for its reliance on heavy machinery and manual labor, is undergoing a dramatic transformation. This revolution is being driven by the rapid advancements in telecommunications, which are enabling manufacturers to optimize their operations, enhance efficiency, and unlock new levels of innovation. From smart factories to predictive maintenance, the impact of telecommunications on the manufacturing sector is profound and far-reaching.
The Rise of the Connected Factory
The foundation of this transformation lies in the concept of the "connected factory," where every aspect of the production process is interconnected through a network of sensors, machines, and software. This connectivity empowers manufacturers to gain real-time insights into their operations, enabling them to:
- Monitor production lines: Sensors embedded in machines collect data on performance, resource consumption, and potential issues, allowing for proactive maintenance and optimization.
- Track inventory and supply chain: Real-time data on inventory levels and supplier performance allows for streamlined logistics and reduced downtime.
- Optimize production processes: By analyzing data from various sources, manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, improve workflow, and enhance overall efficiency.
- Enable remote collaboration: Telecommunications technologies facilitate seamless communication and collaboration between teams, regardless of location, fostering innovation and knowledge sharing.
Key Telecommunications Technologies Driving Manufacturing Innovation
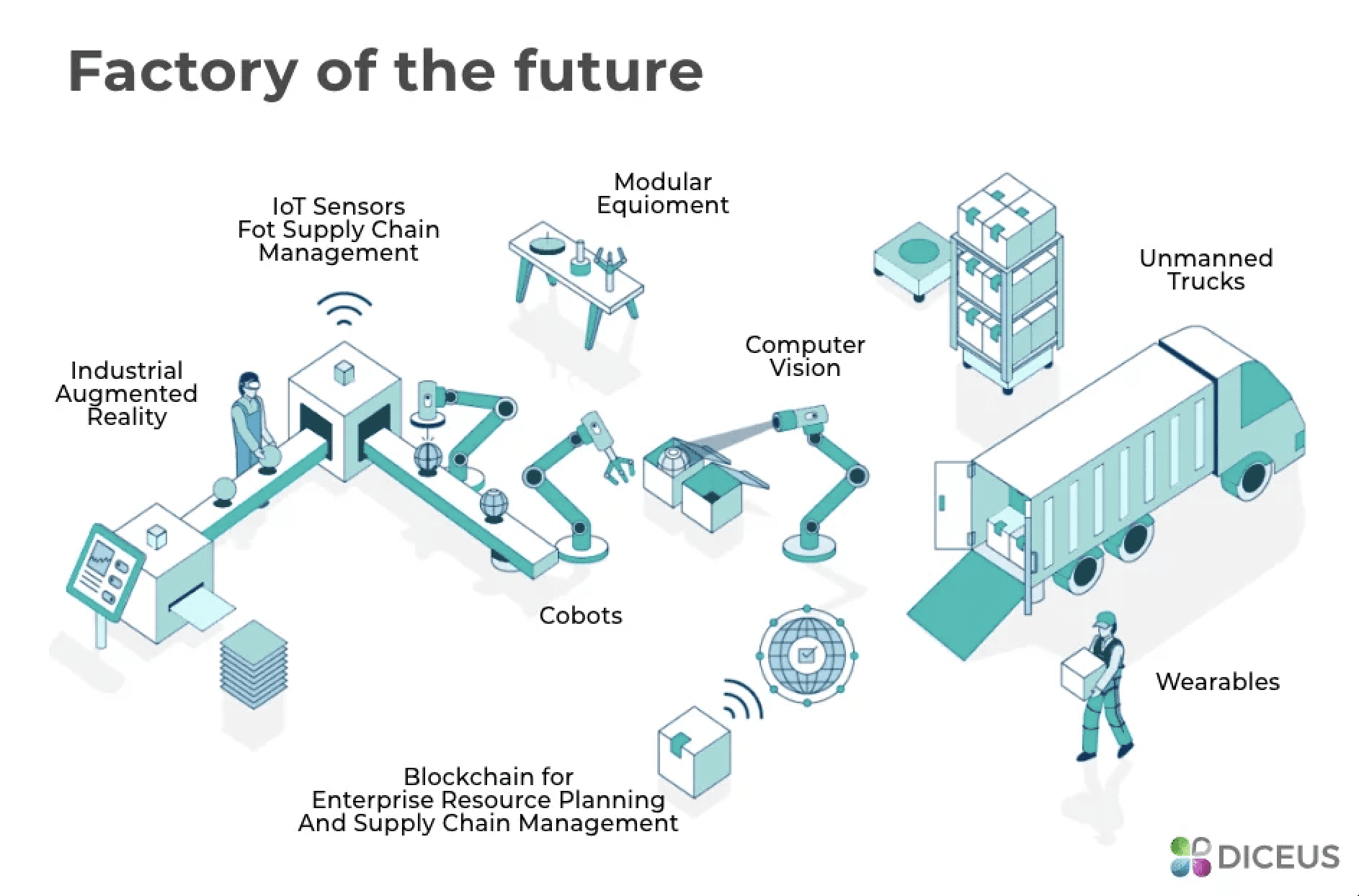
Several key telecommunications technologies are driving the digital transformation of the manufacturing sector in the U.S.:
1. 5G Networks: 5G networks offer unparalleled speed, low latency, and high bandwidth, enabling real-time data transmission and control of complex manufacturing processes. This allows for the deployment of advanced applications like:
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT): Connecting a vast number of sensors and devices, enabling real-time data collection and analysis for predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization.
- Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs): Autonomous robots that navigate factory floors, transporting materials and products with precision and efficiency.
- Remote operation and control: Enabling operators to remotely monitor and control machines and processes, reducing downtime and improving safety.
2. Cloud Computing: Cloud platforms provide manufacturers with scalable and cost-effective computing power, storage, and software solutions. This enables them to:
- Store and analyze massive datasets: Leveraging cloud-based analytics platforms, manufacturers can gain insights from production data to improve decision-making and optimize operations.
- Deploy advanced software applications: Cloud platforms provide access to a wide range of industry-specific software solutions, including ERP, MES, and PLM, streamlining operations and improving efficiency.
- Reduce IT infrastructure costs: By outsourcing their IT infrastructure to the cloud, manufacturers can reduce capital expenditures and focus on core business activities.
3. Edge Computing: Edge computing brings data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and enabling real-time decision-making. This is particularly beneficial for:
- Real-time process control: Enabling immediate responses to changes in production conditions, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime.
- Autonomous operations: Empowering robots and machines to make decisions independently based on real-time data, increasing flexibility and agility.
- Improved cybersecurity: Processing data locally reduces the risk of data breaches and security vulnerabilities associated with cloud-based solutions.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms are being integrated into manufacturing processes to automate tasks, optimize production, and improve quality control. This includes applications like:
- Predictive maintenance: AI algorithms analyze sensor data to predict equipment failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Quality control: AI-powered vision systems can inspect products for defects, ensuring high quality and reducing human error.
- Process optimization: AI algorithms can analyze data to identify bottlenecks and suggest improvements in production processes, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
5. Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology is gaining traction in the manufacturing sector, offering enhanced security, transparency, and traceability. This can be used for:
- Supply chain management: Tracking the origin and movement of materials and products, ensuring authenticity and transparency throughout the supply chain.
- Inventory management: Providing a secure and tamper-proof record of inventory levels, reducing fraud and improving efficiency.
- Data security: Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access and manipulation, enhancing trust and accountability.
The Benefits of Telecommunications in Manufacturing
The adoption of these telecommunications technologies is bringing numerous benefits to the U.S. manufacturing sector, including:
- Enhanced efficiency: Real-time data analysis and automation streamline operations, reduce waste, and improve productivity.
- Improved quality control: AI-powered inspection systems and data-driven insights ensure consistent product quality, reducing defects and customer complaints.
- Increased flexibility and agility: Cloud-based solutions and automated systems allow manufacturers to adapt quickly to changing market demands and production requirements.
- Reduced costs: Optimizing processes, reducing waste, and automating tasks lead to significant cost savings.
- Enhanced safety: Remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automated systems reduce the risk of accidents and injuries in the workplace.
- New product and service offerings: Telecommunications technologies enable manufacturers to develop innovative products and services that meet evolving customer needs.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of telecommunications in manufacturing are undeniable, there are also challenges and considerations to address:
- Cybersecurity: The increasing connectivity of manufacturing systems creates new vulnerabilities to cyberattacks. Robust security measures are essential to protect sensitive data and prevent disruptions to operations.
- Data privacy: The collection and use of vast amounts of data raise concerns about privacy and data security. Manufacturers must comply with regulations and ensure responsible data management practices.
- Skill gaps: The adoption of new technologies requires a skilled workforce with expertise in data analysis, software development, and automation. Bridging the skill gap through training and education is crucial for successful implementation.
- Investment costs: Implementing advanced telecommunications technologies can involve significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and training. Manufacturers need to carefully assess the ROI and prioritize investments based on their specific needs and resources.
Expert Insights
"The future of manufacturing is digital," says [Expert Name], CEO of [Company Name]. "Telecommunications technologies are enabling manufacturers to become more efficient, agile, and innovative. By embracing these advancements, U.S. manufacturers can compete effectively in the global marketplace and drive economic growth."
"The key to successful digital transformation is a holistic approach," adds [Expert Name], Head of Manufacturing Solutions at [Company Name]. "It’s not just about technology; it’s about changing organizational culture, fostering collaboration, and empowering employees to leverage data and technology to their advantage."
Trends and Advancements
The telecommunications landscape is constantly evolving, and new trends and advancements are continuously emerging, further impacting the manufacturing sector:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML algorithms are becoming increasingly sophisticated, enabling manufacturers to automate more complex tasks, optimize processes, and make more informed decisions.
- Internet of Things (IoT) and Edge Computing: The convergence of IoT and edge computing is driving the development of more intelligent and autonomous manufacturing systems, enabling real-time data analysis and control.
- Cloud-native technologies: Cloud-based solutions are becoming increasingly integrated with manufacturing processes, offering greater scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- 5G and Beyond: The rollout of 5G networks is paving the way for even faster and more reliable data transmission, enabling the deployment of more advanced and demanding applications in manufacturing.
- Digital Twins: Digital twins are virtual representations of physical assets, allowing manufacturers to simulate and optimize production processes, reduce downtime, and improve efficiency.
Case Studies
Numerous U.S. manufacturers are successfully leveraging telecommunications technologies to transform their operations and achieve significant results:
- [Company Name] implemented a cloud-based ERP system, streamlining operations and reducing administrative costs.
- [Company Name] deployed AI-powered predictive maintenance systems, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of equipment.
- [Company Name] integrated robotics and automation into their production lines, increasing efficiency and productivity.
Conclusion
Telecommunications technologies are playing a pivotal role in the digital transformation of the manufacturing sector in the U.S. By embracing these advancements, manufacturers can enhance efficiency, improve quality, reduce costs, and unlock new levels of innovation. The future of manufacturing is digital, and those who embrace the opportunities presented by telecommunications will be best positioned to thrive in the years to come.
FAQ
Q: What are the key benefits of using telecommunications in manufacturing?
A: Telecommunications in manufacturing offer numerous benefits, including enhanced efficiency, improved quality control, increased flexibility and agility, reduced costs, enhanced safety, and new product and service offerings.
Q: What are the challenges associated with implementing telecommunications in manufacturing?
A: Challenges include cybersecurity concerns, data privacy issues, skill gaps, and investment costs.
Q: What are some examples of telecommunications technologies used in manufacturing?
A: Examples include 5G networks, cloud computing, edge computing, AI, blockchain technology, and digital twins.
Q: How can manufacturers overcome the challenges of adopting telecommunications technologies?
A: Manufacturers can overcome challenges by investing in robust cybersecurity measures, prioritizing data privacy, bridging the skill gap through training and education, and carefully assessing the ROI of investments.
Q: What are some future trends in telecommunications for the manufacturing sector?
A: Future trends include advancements in AI and ML, the convergence of IoT and edge computing, cloud-native technologies, 5G and beyond, and the adoption of digital twins.
References:
- [Source URL 1]
- [Source URL 2]
- [Source URL 3]
Note: Please replace the bracketed information in the article with specific company names, expert names, and relevant URLs to provide a comprehensive and accurate overview of the topic.
Conclusion
We appreciate your attention to our article and hope you found it informative and useful.