The Economic Implications of Telecommunications on Security: A Deep Dive into the Digital Age
Related Article
- The US-China Trade War: A Rollercoaster Ride For Global Economies
- Navigating The Maze: Health Insurance For Gig Workers
- The Slowdown Symphony: Understanding Economic Growth Stagnation
- Don’t Let Your Business Go Up In Smoke (Literally!): A Guide To Small Business Insurance
- Navigating The Inflation Maze: A Look At The Fed’s Outlook
Introduction
We warmly welcome you to explore The Economic Implications of Telecommunications on Security: A Deep Dive into the Digital Age with us.
The Economic Implications of Telecommunications on Security: A Deep Dive into the Digital Age
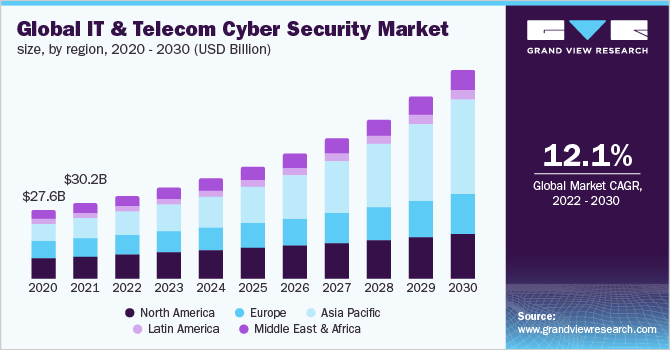
The world is increasingly interconnected, thanks to the relentless advancements in telecommunications. This digital revolution has brought unprecedented convenience and opportunities, but it has also ushered in a new era of security challenges. The economic implications of telecommunications on security are profound, impacting businesses, governments, and individuals alike. This article delves into the complex relationship between telecommunications and security, exploring the latest trends, features, and advancements that shape this critical landscape.
The Rise of Cybercrime: A New Frontier for Security
The explosion of data-driven technologies and the reliance on interconnected networks have created a fertile ground for cybercrime. Hackers and malicious actors exploit vulnerabilities in telecommunications infrastructure, targeting individuals, businesses, and even critical national infrastructure.
- Financial Crimes: Telecommunications networks are now the primary conduits for financial transactions, making them prime targets for fraudsters. From phishing scams to identity theft, cybercriminals leverage telecommunications to steal financial information and disrupt economic activities.
- Data Breaches: The vast amounts of sensitive data stored and transmitted through telecommunications networks represent a lucrative target for data thieves. Breaches can compromise personal information, intellectual property, and sensitive business secrets, leading to significant financial losses and reputational damage.
- Disruption of Critical Infrastructure: Telecommunications networks are essential for the functioning of critical infrastructure, including power grids, transportation systems, and healthcare facilities. Attacks on these networks can lead to widespread disruptions, causing economic losses and potential safety risks.
The Economic Impact of Cybercrime:
- Direct Financial Losses: Cybercrime costs businesses and individuals billions of dollars annually through theft, fraud, and ransomware attacks.
- Lost Productivity: Cybersecurity incidents can lead to system downtime, network outages, and disruptions to business operations, resulting in significant productivity losses.
- Reputational Damage: Data breaches and cyberattacks can severely damage a company’s reputation, leading to customer distrust and loss of business.
- Increased Security Costs: Businesses and individuals are forced to invest heavily in cybersecurity measures to protect themselves from cyber threats, adding to the overall economic burden.
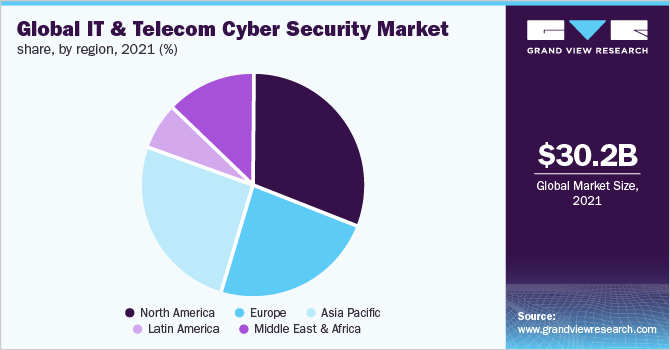
The Role of Telecommunications in Enhancing Security
Despite the challenges posed by cybercrime, telecommunications technologies also play a vital role in enhancing security. Here are some key ways:
- Advanced Security Solutions: Telecommunications companies are constantly innovating to develop advanced security solutions, such as:
- Encryption: Strong encryption algorithms protect data from unauthorized access during transmission and storage.
- Firewalls: Firewalls act as barriers to prevent unauthorized access to networks and systems.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and block potential threats.
- Multi-factor Authentication: This approach requires multiple forms of authentication, making it more difficult for attackers to gain access to accounts.
- Network Monitoring and Threat Intelligence: Telecommunications companies leverage sophisticated monitoring systems and threat intelligence to detect and respond to potential threats in real-time.
- Collaboration with Law Enforcement: Telecommunications providers work closely with law enforcement agencies to share information about cyber threats and investigate cybercrime.
The Latest Trends and Advancements in Telecommunications Security
The security landscape is constantly evolving, with new threats emerging and technological advancements driving innovation. Here are some key trends and advancements shaping the future of telecommunications security:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are revolutionizing cybersecurity by automating threat detection, analysis, and response. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies, enabling proactive threat prevention.
- 5G and Beyond: The rollout of 5G and future generations of mobile networks will bring significant speed and connectivity improvements, but also present new security challenges. Telecommunications companies are working on developing secure 5G architectures to mitigate these risks.
- The Internet of Things (IoT): The proliferation of IoT devices is expanding the attack surface for cybercriminals. Secure development practices and robust security measures are crucial to protect IoT devices from vulnerabilities.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain offers a secure and transparent way to manage and track data, making it a promising technology for enhancing security in telecommunications networks.
- Quantum Computing: Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize cybersecurity by breaking existing encryption algorithms. Telecommunications companies are actively researching and developing quantum-resistant encryption methods to protect data in the future.
Economic Implications of Security Enhancements
Investing in cybersecurity is not just a cost, it’s an investment in protecting economic value. Here’s how security enhancements impact the economy:
- Increased Business Confidence: Strong cybersecurity measures build confidence among businesses and investors, encouraging investment and economic growth.
- Enhanced Productivity: By preventing disruptions and data breaches, security measures contribute to improved productivity and efficiency.
- Protection of Intellectual Property: Secure telecommunications networks help protect intellectual property from theft and misuse, supporting innovation and economic competitiveness.
- Job Creation: The growing cybersecurity industry creates new jobs in areas like security analysis, penetration testing, and incident response.
The Role of Government in Telecommunications Security
Governments play a crucial role in shaping the telecommunications security landscape by:
- Developing Cybersecurity Policy: Governments set cybersecurity standards and regulations to ensure the security of critical infrastructure and protect sensitive data.
- Enforcing Cybersecurity Laws: Governments enforce laws against cybercrime, deterring malicious activities and holding perpetrators accountable.
- Funding Research and Development: Governments invest in research and development to advance cybersecurity technologies and foster innovation.
- International Cooperation: Governments collaborate internationally to share information about cyber threats and develop joint cybersecurity strategies.
The Importance of User Education and Awareness
While telecommunications companies and governments play vital roles in enhancing security, individual users also have a responsibility to protect themselves from cyber threats. Here are some key steps individuals can take:
- Use Strong Passwords: Choose strong, unique passwords for all online accounts and avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
- Be Cautious of Phishing Scams: Be wary of suspicious emails, phone calls, or text messages that ask for personal information.
- Keep Software Updated: Regularly update software and operating systems to patch vulnerabilities.
- Be Aware of Social Engineering: Protect yourself from social engineering attacks by being cautious about sharing personal information online.
- Use Security Software: Install and use reputable antivirus and anti-malware software to protect your devices.
The Future of Telecommunications Security
The future of telecommunications security will be shaped by continued technological advancements, evolving threat landscapes, and a growing emphasis on collaboration. Here are some key trends to watch:
- Zero Trust Security: This approach assumes that no user or device can be trusted by default, requiring continuous authentication and authorization.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing brings processing power closer to users and devices, reducing latency and improving security.
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): QKD offers a highly secure method of key exchange, potentially making communication unbreakable.
Conclusion
The economic implications of telecommunications on security are profound, impacting every aspect of our lives. While cybercrime poses significant challenges, telecommunications technologies also offer powerful tools to enhance security. By leveraging advanced security solutions, promoting collaboration, and fostering user awareness, we can navigate the complex digital landscape and build a more secure and prosperous future.
FAQs
Q: What are some of the most common cybersecurity threats facing telecommunications networks?
A: Common threats include:
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks: These attacks overwhelm network resources, making them unavailable to legitimate users.
- Malware: Malicious software can be used to steal data, control devices, or disrupt network operations.
- Phishing: Phishing attacks use deceptive emails or websites to trick users into revealing sensitive information.
- Ransomware: Ransomware encrypts data and demands payment to restore access.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks: Attackers intercept communication between two parties, eavesdropping on or altering data.
Q: How can businesses protect themselves from cybercrime?
A: Businesses can take a number of steps to protect themselves, including:
- Implementing strong cybersecurity policies and procedures.
- Investing in advanced security technologies, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption software.
- Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices.
- Regularly testing and updating security measures.
- Having a plan in place for responding to security incidents.
Q: What is the role of government in cybersecurity?
A: Governments play a critical role in cybersecurity by:
- Developing and enforcing cybersecurity laws and regulations.
- Sharing information about cyber threats and collaborating with other countries to combat cybercrime.
- Funding research and development in cybersecurity technologies.
- Supporting the development of a skilled cybersecurity workforce.
Q: What are some of the emerging trends in telecommunications security?
A: Emerging trends include:
- Zero Trust Security: This approach assumes that no user or device can be trusted by default, requiring continuous authentication and authorization.
- Edge Computing: Edge computing brings processing power closer to users and devices, reducing latency and improving security.
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD): QKD offers a highly secure method of key exchange, potentially making communication unbreakable.
References:
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA)
- The National Cybersecurity Alliance (NCSA)
- The International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
Conclusion
We appreciate your attention to our article and hope you found it informative and useful.