Impact of Fed Rate Hike on the U.S. Economy
Related Article
- The Rising Tide: Navigating The Increase In Auto Insurance Deductibles
- The Power Of Connection: How Telecommunications Fuels Global Trade
- Economic Strategies For The Telecommunications Industry
- The Looming Shadow: Risks Of A US Housing Market Crash
- The Looming Shadow: A Deep Dive Into The US Corporate Debt Crisis
Introduction
We’re thrilled to guide you through Impact of Fed Rate Hike on the U.S. Economy as we dive into the essentials of economics, giving you all the insights you need to stay informed.
The Fed’s Rate Hike: A Rollercoaster Ride for the U.S. Economy

The Federal Reserve (Fed), the central bank of the United States, wields immense power over the nation’s economy through its monetary policy tools. One of the most impactful tools in its arsenal is the federal funds rate, the interest rate at which banks lend reserves to each other overnight. When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, it becomes more expensive for banks to borrow money, which can trickle down to impact various aspects of the economy.
What’s the Big Deal with Rate Hikes?
Imagine the economy as a delicate balancing act. The Fed’s rate hikes are like adjusting the weight on one side of the scale. The goal is to keep inflation under control while ensuring economic growth remains healthy.
Here’s how rate hikes impact the economy:
1. Cooling Inflation:
- Higher borrowing costs: When rates go up, borrowing money becomes more expensive for businesses and consumers. This can slow down spending and investment, reducing demand for goods and services.
- Reduced money supply: Higher rates discourage banks from lending, leading to a decrease in the money supply. Less money in circulation can help curb inflation.
- Stronger dollar: Higher rates attract foreign investment, making the dollar stronger. This can make imports cheaper and exports more expensive, potentially further cooling inflation.
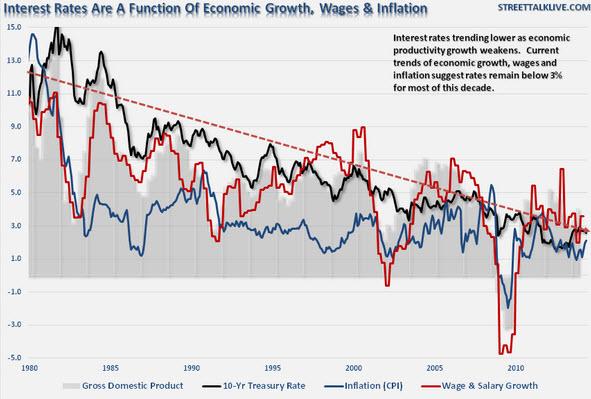
2. Economic Growth Slowdown:
- Reduced investment: Higher borrowing costs can make businesses hesitant to invest in new projects or expand operations.
- Slower consumer spending: With higher interest rates on loans, consumers might delay big purchases like cars or homes. This can lead to a slowdown in consumer spending, which drives a significant portion of the U.S. economy.
- Potential for recession: If rate hikes are too aggressive or prolonged, they can push the economy into a recession.
The Latest Fed Moves: A Tale of Two Eras
The Fed has been on a rate-hiking spree since March 2022, aiming to tame the highest inflation in decades. The aggressive approach has been met with mixed reactions, with some praising the Fed’s efforts to control inflation, while others worry about the potential for a recession.
Here’s a breakdown of the recent Fed rate hikes:
- 2022: The Fed raised rates by 4.25% throughout the year, the most aggressive tightening cycle since the 1980s.
- 2023: The Fed continued its rate-hiking campaign, raising rates by another 0.5% in the first half of the year.
The Future of the Fed’s Policy: A Balancing Act
The Fed is now walking a tightrope, trying to balance the need to control inflation with the risk of triggering a recession.
Here are some key factors influencing the Fed’s decision-making:
- Inflation data: The Fed closely monitors inflation data to gauge the effectiveness of its rate hikes.
- Economic growth: The Fed wants to ensure that rate hikes don’t stifle economic growth.
- Labor market conditions: A strong labor market with low unemployment can support higher rates, but a weakening labor market might require a more cautious approach.
- Global economic outlook: The Fed also considers global economic conditions, as they can impact the U.S. economy.
Expert Insights on the Fed’s Rate Hike Impact
- "The Fed’s rate hikes are a necessary evil to combat inflation, but they will inevitably slow down economic growth. The key is to find the right balance to avoid a recession." – Dr. Janet Yellen, former Federal Reserve Chair
- "The Fed is facing a difficult challenge. They need to be aggressive enough to tame inflation but not so aggressive that they trigger a recession. It’s a delicate balancing act." – Dr. Larry Summers, former Treasury Secretary
Navigating the Rate Hike Rollercoaster: Tips for Individuals and Businesses
For Individuals:
- Review your finances: Assess your debt obligations and consider refinancing if possible to lower your interest rates.
- Save more: With higher interest rates, your savings can earn more.
- Invest wisely: Consider diversifying your investments to mitigate risks.
For Businesses:
- Manage cash flow: Monitor your cash flow closely and adjust your operations to adapt to higher borrowing costs.
- Negotiate with suppliers: Explore ways to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Consider alternative financing: Explore alternative financing options if traditional loans are too expensive.
The Impact of Rate Hikes on Different Sectors:
Housing Market:
- Higher mortgage rates: Rate hikes lead to higher mortgage rates, making homeownership more expensive.
- Reduced demand: This can lead to a slowdown in home sales and a potential decline in home prices.
Stock Market:
- Volatility: Rate hikes can create uncertainty and volatility in the stock market.
- Potential for decline: Higher rates can make companies less attractive to investors, potentially leading to a decline in stock prices.
Consumer Spending:
- Reduced spending: Higher interest rates on loans can discourage consumers from making big purchases.
- Shifting consumer behavior: Consumers may prioritize paying down debt or saving more, leading to a shift in spending patterns.
The Future of the Fed’s Rate Hikes: A Look Ahead
The Fed’s rate-hiking path remains uncertain, with many factors influencing its future decisions. The Fed will likely continue to adjust rates based on economic data and its assessment of the inflation outlook.
Key questions for the future:
- How long will the Fed continue to raise rates?
- Will the Fed eventually pivot to cutting rates?
- What impact will the Fed’s rate hikes have on the U.S. economy in the long term?
Conclusion:
The Fed’s rate hikes are a powerful tool for managing the U.S. economy. While they can help control inflation, they also come with risks, including slowing economic growth and potentially triggering a recession. The Fed is navigating a complex landscape, and its decisions will have a significant impact on businesses, individuals, and the overall economy.
FAQ:
1. Why does the Fed raise interest rates?
The Fed raises interest rates to control inflation. Higher rates make it more expensive to borrow money, which can slow down spending and reduce demand for goods and services.
2. How do rate hikes impact the housing market?
Rate hikes lead to higher mortgage rates, making homeownership more expensive. This can reduce demand for homes, leading to a slowdown in sales and a potential decline in prices.
3. Can rate hikes cause a recession?
Yes, if rate hikes are too aggressive or prolonged, they can push the economy into a recession.
4. What can individuals do to prepare for rate hikes?
Individuals can review their finances, consider refinancing debt, save more, and invest wisely.
5. What can businesses do to prepare for rate hikes?
Businesses can manage cash flow, negotiate with suppliers, and explore alternative financing options.
References:
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Please consult with a qualified financial professional before making any investment decisions.
Conclusion
Keep following us for more in-depth guides, expert tips, and the latest updates to keep you ahead in understanding the world of economics. Until next time, stay curious and engaged, and we’ll see you in our next deep dive!