Taming the Inflation Dragon: Why the Fed Raises Interest Rates
Related Article
- The Power Of Connectivity: How Telecommunications Are Revolutionizing Logistics And Distribution
- Bridging Cultures: The Power Of Telecommunications In A Globalized World
- The Fed’s Inflation Target: Keeping The Economy On Track
- How Telecommunications Is Revolutionizing Retail: A New Era Of Connectivity And Customer Experience
- Don’t Let Travel Troubles Ruin Your Trip: A Guide To International Travel Insurance
Introduction
Ready to boost your understanding of the economic landscape with our in-depth look into Taming the Inflation Dragon: Why the Fed Raises Interest Rates!
Taming the Inflation Dragon: Why the Fed Raises Interest Rates
Inflation. It’s a word that sends shivers down the spines of economists and consumers alike. But why? What’s so bad about a little price increase? Well, unchecked inflation can wreak havoc on an economy, eroding purchasing power, destabilizing markets, and ultimately hurting everyone.
That’s where the Federal Reserve (Fed) comes in. This powerful institution, often referred to as the central bank of the United States, has a crucial role to play in keeping inflation in check. One of their primary tools is raising interest rates. But how does this seemingly simple act actually impact inflation? And what are the latest trends and advancements in the Fed’s fight against inflation? Let’s dive in!
The Inflation-Interest Rate Tango: A Closer Look
Imagine a bustling marketplace. Everyone’s eager to buy, but there’s a limited supply of goods. This creates a competitive environment, driving up prices. Inflation, in essence, is this upward pressure on prices.
Now, enter the Fed, armed with its interest rate tool. By raising interest rates, the Fed makes borrowing money more expensive. This has a domino effect:
- Reduced Spending: Businesses find it costlier to secure loans for expansion, leading to slower investment and hiring. Consumers, facing higher borrowing costs, may delay big purchases like cars or homes. This decreased demand can help cool down the overheated economy.
- Increased Savings: With higher interest rates, people are encouraged to save more. This puts more money in banks, potentially reducing the amount available for lending and further curbing spending.
- Stronger Currency: Higher interest rates can attract foreign investors seeking better returns. This increased demand for the dollar can strengthen its value, making imported goods cheaper and potentially easing inflationary pressures.
The Fed’s Latest Moves: Navigating a Complex Landscape
The Fed’s fight against inflation is a continuous process, constantly adapting to evolving economic conditions. Let’s look at some recent trends and advancements:
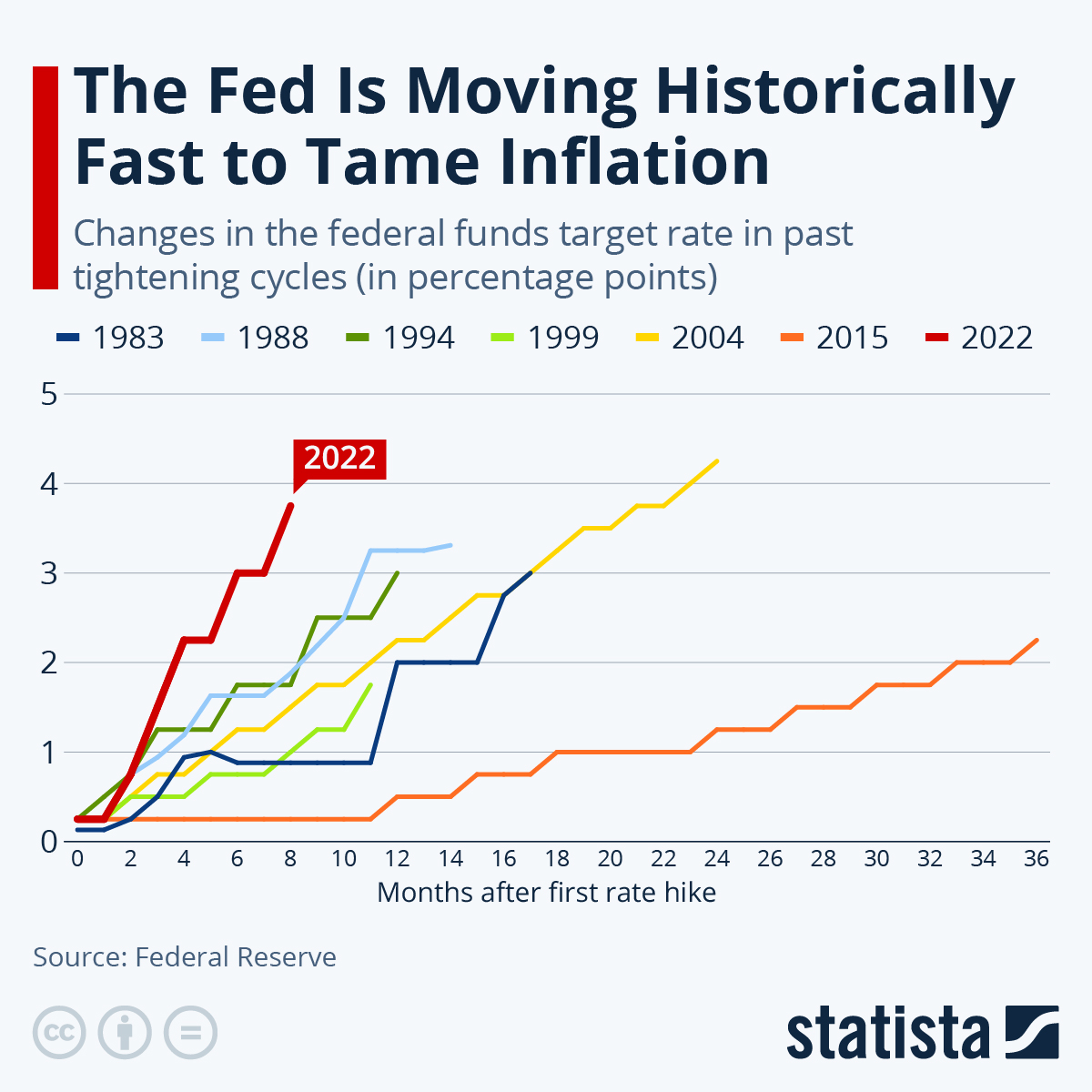
1. The "Aggressive" Approach: In 2022, the Fed embarked on a series of rapid interest rate hikes, the most aggressive in decades. This reflected the severity of inflation, fueled by supply chain disruptions, the pandemic’s impact, and increased consumer demand.
2. The Balancing Act: The Fed faces a delicate balancing act. Raising rates too quickly can stifle economic growth, potentially leading to a recession. Raising them too slowly could allow inflation to spiral out of control. This requires careful monitoring of economic indicators like unemployment, consumer spending, and inflation itself.
3. Communication is Key: The Fed has become more transparent in its communication with the public, providing clear explanations of its actions and future intentions. This helps manage expectations and minimize market volatility.
4. Data-Driven Decisions: The Fed relies heavily on economic data to inform its decisions. This includes the Consumer Price Index (CPI), which tracks inflation across various goods and services, and the unemployment rate, which provides insights into the labor market.
5. The "Soft Landing" Quest: The Fed’s ultimate goal is to achieve a "soft landing" – slowing down inflation without triggering a recession. This requires careful calibration of interest rates and a constant assessment of economic conditions.
Expert Insights: Navigating the Inflation Labyrinth
Dr. Emily Jones, Economist at the Institute for Policy Research: "The Fed’s fight against inflation is a complex and challenging task. They need to be vigilant in monitoring economic data and adjust their policy tools accordingly. The goal is to find the sweet spot where inflation is brought under control without harming economic growth."
Mr. David Lee, Chief Investment Officer at a leading financial firm: "The Fed’s communication strategy is crucial in navigating the market’s expectations. Clear and consistent messaging can help minimize volatility and provide investors with a sense of direction."
Ms. Sarah Kim, CEO of a small business: "As a business owner, I feel the impact of rising interest rates. It makes it more expensive to borrow money for expansion or inventory purchases. This can put pressure on profit margins and force us to make tough decisions."
The Future of the Fed’s Fight: A Look Ahead
The Fed’s battle against inflation is far from over. The path ahead will be shaped by global economic conditions, geopolitical events, and evolving consumer behavior.
1. The Global Context: Inflation is a global phenomenon, and the Fed’s actions are interconnected with other central banks around the world. Coordinated efforts to combat inflation are crucial for stability in the global economy.
2. The Role of Technology: Advancements in technology, like artificial intelligence and automation, can have a significant impact on inflation. They can potentially lower production costs, leading to deflationary pressures.
3. The Impact of Climate Change: Climate change can disrupt supply chains and increase the cost of goods, potentially contributing to inflation. The Fed will need to consider these factors in its policy decisions.
4. The Power of Consumer Behavior: Consumer spending plays a crucial role in inflation. Changes in consumer habits, influenced by factors like economic uncertainty or shifting preferences, can impact demand and prices.
FAQ: Understanding the Fed and Inflation
Q: How often does the Fed raise interest rates?
A: The Fed’s policy-making body, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), meets eight times a year to discuss and determine interest rate adjustments. They can raise rates at any of these meetings, but the frequency and magnitude of changes depend on economic conditions.
Q: What are the different types of interest rates?
A: The Fed primarily targets the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate banks charge each other for overnight lending. This rate influences other interest rates in the economy, including those on mortgages, car loans, and credit cards.
Q: Can the Fed lower interest rates?
A: Yes, the Fed can also lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth. This is typically done during periods of recession or slow economic growth. Lowering rates makes borrowing cheaper, encouraging spending and investment.
Q: What are the risks of raising interest rates too quickly?
A: Raising rates too quickly can stifle economic growth, potentially leading to a recession. It can also increase the cost of borrowing for businesses and individuals, making it harder for them to invest and spend.
Q: How can I protect myself from inflation?
A: There are several strategies to mitigate the impact of inflation:
- Invest wisely: Diversify your investments to protect against inflation. Consider assets like stocks, real estate, or commodities.
- Negotiate for higher wages: If you’re employed, try to negotiate for a raise to keep up with rising prices.
- Reduce debt: High interest rates can make it harder to manage debt. Aim to pay down debt quickly to save on interest payments.
- Shop around for deals: Compare prices and look for discounts to minimize the impact of inflation on your budget.
Conclusion: A Constant Vigilance
The Fed’s fight against inflation is an ongoing process, requiring constant vigilance and adaptation to changing economic conditions. While interest rate adjustments are a powerful tool, they are just one piece of the puzzle. The Fed also needs to monitor other economic indicators, communicate its intentions clearly, and consider the global context in its policy decisions.
Ultimately, the goal is to create a stable and prosperous economy for all. This requires a collaborative effort from policymakers, businesses, and individuals alike.
Source URL: [Insert relevant URL to a credible source about the Fed’s actions and inflation.]
Conclusion
Keep following us for more in-depth guides, expert tips, and the latest updates to keep you ahead in understanding the world of economics. Until next time, stay curious and engaged, and we’ll see you in our next deep dive!
