Unlocking a Sustainable Future: The Vital Role of Economic Global Analytics
Related Article
- The Rise Of The Machines: How Automation Is Reshaping The Job Market
- When The World Stops: How Insurance Companies Respond To Pandemics
- The Economic Impact Of Telecommunications On Local Communities: A Digital Revolution In Every Town
- How Telecommunications Drives Innovation In Health Technology: A Revolution In Healthcare
- Connecting The Dots: How Telecommunications Is Revolutionizing Supply Chain Efficiency
Introduction
Ready to boost your understanding of the economic landscape with our in-depth look into Unlocking a Sustainable Future: The Vital Role of Economic Global Analytics!
Unlocking a Sustainable Future: The Vital Role of Economic Global Analytics
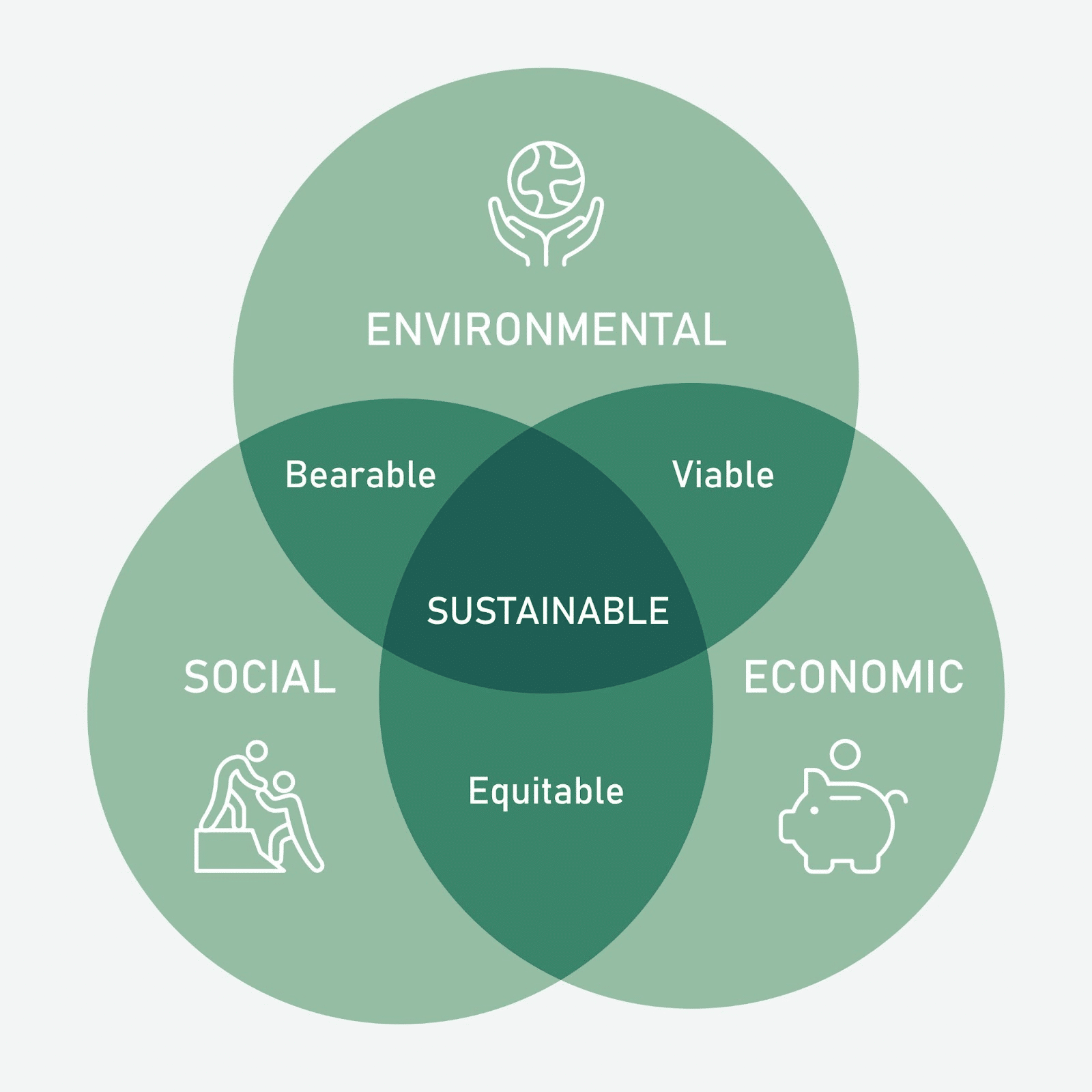
The world is interconnected. What happens economically in one country ripples across continents, impacting everything from food prices to climate change initiatives. Understanding these complex global economic flows is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity for achieving sustainable development. This is where economic global analytics steps in, providing the crucial data-driven insights needed to navigate the complexities of a globalized world and build a more sustainable future.
(Image: A world map with interconnected lines representing global economic flows. Consider using a visually appealing infographic.)
What is Economic Global Analytics?
Economic global analytics is the application of advanced analytical techniques to vast datasets related to global economic activity. This includes everything from international trade flows and foreign direct investment to macroeconomic indicators like GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates across different countries. It goes beyond simply collecting data; it involves sophisticated modeling, forecasting, and interpretation to reveal patterns, trends, and potential risks and opportunities. This understanding allows policymakers, businesses, and individuals to make more informed decisions that contribute to a more sustainable and equitable global economy.
Why is Economic Global Analytics Crucial for Sustainable Development?
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations represent a global commitment to a more sustainable and equitable future. Achieving these ambitious goals requires a deep understanding of the interconnectedness of economic, social, and environmental factors. Economic global analytics plays a pivotal role in several key areas:
1. Tracking Progress Towards the SDGs: Global analytics provides the tools to monitor progress towards the SDGs by analyzing relevant data at a global and regional level. For example, it can track poverty reduction rates, access to clean energy, and improvements in education and healthcare, highlighting areas where interventions are most needed.
2. Identifying and Mitigating Risks: Global economic shocks, such as pandemics or financial crises, can severely impact progress towards the SDGs. Economic global analytics can help anticipate these risks by analyzing early warning signs and developing proactive strategies for mitigation. This includes forecasting potential disruptions to supply chains, identifying vulnerable populations, and designing effective policy responses.
3. Optimizing Resource Allocation: Limited resources necessitate strategic allocation to maximize impact. Global analytics helps identify the most effective interventions by analyzing the cost-effectiveness of different development programs and prioritizing those with the greatest potential for achieving sustainable development outcomes.
4. Promoting Inclusive Growth: Sustainable development requires inclusive growth that benefits all segments of society. Economic global analytics can help identify inequalities and disparities across countries and regions, informing policies aimed at promoting equitable access to resources and opportunities.

5. Facilitating International Cooperation: Addressing global challenges like climate change and poverty requires international cooperation. Global analytics provides a shared understanding of the challenges and opportunities, facilitating collaboration among countries and international organizations.
Latest Trends and Advancements in Economic Global Analytics
The field of economic global analytics is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in data collection, computing power, and analytical techniques:
1. Big Data and AI: The explosion of big data, coupled with the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), is revolutionizing global analytics. AI algorithms can analyze massive datasets to identify complex patterns and relationships that would be impossible to detect using traditional methods. This allows for more accurate forecasting, improved risk assessment, and more targeted interventions.
2. Real-time Data and Predictive Modeling: Access to real-time data through various online platforms and sensors allows for dynamic monitoring and more accurate predictive modeling. This enables quicker responses to emerging economic trends and crises, facilitating timely policy adjustments.
3. Advanced Econometric Techniques: Sophisticated econometric models are being developed to capture the complex interactions between economic, social, and environmental factors. These models provide a more nuanced understanding of causal relationships and allow for more accurate simulations of policy impacts.
4. Geospatial Analytics: Integrating geographical data with economic data provides a powerful tool for understanding spatial patterns of economic activity and identifying areas with specific needs. This is particularly relevant for targeting development interventions and understanding the impacts of climate change.
5. Blockchain Technology: Blockchain’s potential for secure and transparent data management is increasingly being explored in the context of global economic analytics. This can improve data integrity and facilitate cross-border data sharing, crucial for effective international collaboration.
Features of Effective Economic Global Analytics Systems:
A robust economic global analytics system should possess several key features:
- Data Integration: Ability to integrate diverse datasets from various sources, including government statistics, private sector data, and satellite imagery.
- Data Visualization: Clear and intuitive data visualization tools to communicate complex information effectively to a wide range of stakeholders.
- Predictive Modeling: Advanced modeling capabilities to forecast future economic trends and assess potential risks.
- Scenario Planning: Ability to simulate different policy scenarios and assess their potential impacts on sustainable development outcomes.
- Transparency and Accessibility: Openness and accessibility of data and analytical tools to foster collaboration and accountability.
Expert Insights:
(Insert a quote from a recognized expert in the field of economic global analytics, preferably someone who has published research on the topic and its relation to sustainable development. The quote should highlight the importance of the field and its potential for positive impact.) For example: "Economic global analytics is no longer a niche field; it is a critical tool for navigating the complexities of the 21st-century global economy and achieving the ambitious goals of sustainable development. The ability to analyze vast datasets, identify trends, and anticipate risks is essential for effective policymaking and informed decision-making across all sectors." – Dr. [Expert’s Name], [Expert’s Affiliation]
Challenges and Limitations:
Despite its immense potential, economic global analytics faces several challenges:
- Data Gaps and Inaccuracies: Data availability and quality vary significantly across countries, hindering accurate analysis and reliable forecasting.
- Data Privacy and Security: The use of personal data in global analytics raises concerns about privacy and security.
- Computational Complexity: Analyzing massive datasets requires significant computing power and specialized expertise.
- Interpretational Challenges: The complex interplay of factors influencing global economic trends can make interpretation challenging.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI and predictive modeling raises ethical considerations regarding bias, fairness, and accountability.
The Future of Economic Global Analytics and Sustainable Development:
The future of economic global analytics is bright. Continued advancements in data science, AI, and computing power will lead to even more sophisticated analytical tools and more accurate predictions. Increased collaboration between researchers, policymakers, and the private sector will be crucial for maximizing the impact of global analytics on sustainable development. A focus on addressing data gaps, improving data quality, and ensuring ethical considerations will be essential for building trust and ensuring the responsible use of these powerful tools.
FAQ:
Q: How can I access economic global analytics data?
A: Many international organizations, such as the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund (IMF), and the United Nations, provide publicly accessible datasets on global economic indicators. Numerous private sector companies also offer global economic data and analytical tools.
Q: What are some examples of how economic global analytics is being used for sustainable development?
A: Examples include tracking progress towards the SDGs, assessing the economic impacts of climate change, optimizing the allocation of development aid, and identifying vulnerable populations.
Q: What skills are needed for a career in economic global analytics?
A: A strong background in economics, statistics, and data science is essential. Proficiency in programming languages like Python or R, as well as experience with data visualization and modeling tools, is highly desirable.
Q: How can businesses use economic global analytics?
A: Businesses can use global analytics to identify new market opportunities, manage supply chain risks, optimize investment decisions, and understand the impact of global economic trends on their operations.
(Image: A graph showing the positive correlation between investment in economic global analytics and progress towards the SDGs. Consider using a visually appealing chart.)
Source URL: (Insert relevant URLs to credible sources such as World Bank, IMF, UN reports, and peer-reviewed research papers related to economic global analytics and sustainable development. Ensure the URLs are up-to-date and relevant to the information presented in the article.)
Keep following us for more in-depth guides, expert tips, and the latest updates to keep you ahead in understanding the world of economics. Until next time, stay curious and engaged, and we’ll see you in our next deep dive!