Riding the Waves of Change: A Deep Dive into Flood Insurance Coverage Trends
Related Articles
- The Great American Wealth Divide: Understanding The Distribution Of Riches
- The Renewable Energy Revolution: More Than Just Clean Air, It’s Big Business
- Workers’ Compensation: Your Safety Net When Work Gets Risky
- Fueling The American Engine: A Deep Dive Into US Economic Growth Strategies
- The Fed’s Inflation Target: Keeping The Economy On Track
Introduction
Uncover the latest details about Riding the Waves of Change: A Deep Dive into Flood Insurance Coverage Trends in this comprehensive guide.
Riding the Waves of Change: A Deep Dive into Flood Insurance Coverage Trends
The world is becoming increasingly aware of the devastating effects of climate change, and one of the most visible consequences is the rising frequency and severity of floods. This has led to a significant shift in the landscape of flood insurance coverage, with both homeowners and insurers adapting to the evolving reality of a waterlogged future.
This article will delve into the key trends shaping the flood insurance market, exploring the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. We’ll cover everything from the intricacies of the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) to the rise of private flood insurance options, analyzing how these trends are impacting homeowners and the insurance industry as a whole.
Understanding the Flood Insurance Landscape
Before we dive into the trends, let’s first understand the basics of flood insurance. Unlike standard homeowners insurance, flood coverage is typically purchased separately. This is because most standard policies exclude coverage for flood damage, which is defined as the inundation of normally dry land by water.
The primary source of flood insurance in the United States is the NFIP, a government-backed program administered by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). The NFIP offers flood insurance policies to homeowners and businesses in participating communities nationwide.
Key Trends Shaping the Flood Insurance Market
1. The Growing Need for Flood Insurance
The most significant trend driving the flood insurance market is the increasing frequency and severity of floods. Climate change is leading to rising sea levels, more intense rainfall events, and more frequent storm surges, all of which contribute to a higher risk of flooding.
This reality is pushing more homeowners to consider flood insurance, even in areas not traditionally considered high-risk. According to FEMA, only about 20% of homeowners in flood-prone areas have flood insurance. This means a significant portion of the population is vulnerable to financial hardship in the event of a flood.
2. The Rise of Private Flood Insurance
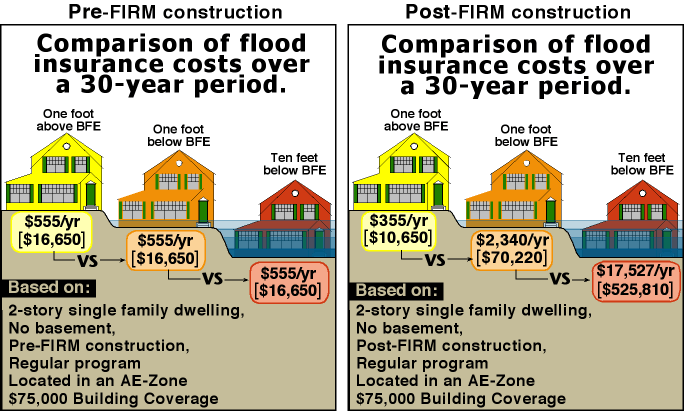
The NFIP has long been the dominant player in the flood insurance market. However, in recent years, private insurers have increasingly stepped into the fray, offering alternative flood insurance options. This trend is driven by several factors, including:
- NFIP reform: The NFIP has faced financial challenges due to increasing flood claims and has undergone several reforms aimed at improving its solvency. These reforms have, in some cases, led to higher premiums and more stringent underwriting standards.
- Increased demand: The growing awareness of flood risk has spurred demand for flood insurance, creating an opportunity for private insurers to enter the market.
- Technological advancements: Advances in data analytics and risk modeling have enabled private insurers to better assess flood risk and offer more competitive pricing.
3. The Shift Towards Risk-Based Pricing
Traditional flood insurance pricing has often been based on location, with premiums varying based on the flood risk of a particular area. However, the rise of private flood insurance and the adoption of advanced risk modeling techniques have led to a shift towards more risk-based pricing.
This means that premiums are now being determined based on a wider range of factors, such as the elevation of the property, the type of construction, and the proximity to flood-prone areas. This move towards risk-based pricing is seen as fairer and more accurate, as it reflects the actual flood risk faced by individual homeowners.
4. The Importance of Flood Mitigation
Flood mitigation strategies are becoming increasingly important in reducing flood risk and lowering insurance premiums. These strategies can include:
- Elevating structures: Raising the foundation of a building above the base flood elevation can significantly reduce the risk of flood damage.
- Installing flood barriers: Flood barriers can be used to protect buildings from rising floodwaters.
- Improving drainage: Enhancing drainage systems can help to prevent water from accumulating around a property.
Homeowners who implement flood mitigation measures can often qualify for discounts on their flood insurance premiums.
5. The Role of Technology
Technology is playing a growing role in the flood insurance market, enabling insurers to:
- Improve risk assessment: Advanced data analytics and risk modeling tools are allowing insurers to better assess flood risk and develop more accurate pricing models.
- Enhance customer service: Online platforms and mobile apps are making it easier for homeowners to obtain quotes, purchase policies, and manage their flood insurance.
- Promote flood preparedness: Technology is being used to develop tools and resources that help homeowners understand their flood risk and prepare for potential flooding events.
Challenges and Opportunities
The evolving flood insurance landscape presents both challenges and opportunities for homeowners and insurers alike.
Challenges:
- Affordability: Flood insurance can be expensive, especially for homeowners in high-risk areas. This can be a barrier to access for many homeowners, particularly those with limited financial resources.
- Coverage gaps: The NFIP and private insurers may not always provide sufficient coverage for all types of flood damage. This can leave homeowners vulnerable to significant financial losses in the event of a major flood.
- Underwriting complexities: Assessing flood risk and developing accurate pricing models can be complex, especially as the frequency and severity of floods increase.
Opportunities:
- Innovation: The growing demand for flood insurance is creating opportunities for insurers to develop innovative products and services that meet the needs of a changing market.
- Collaboration: Collaboration between public and private sector stakeholders can help to address the challenges of flood insurance affordability and coverage gaps.
- Public awareness: Raising public awareness about flood risk and the importance of flood insurance can help to encourage more homeowners to purchase coverage.
FAQ: Flood Insurance Coverage
Q: What does flood insurance cover?
A: Flood insurance covers damage to your building and its contents caused by flooding. This includes damage from:
- Overflowing rivers, streams, and lakes
- Heavy rainfall
- Storm surges
- Coastal flooding
Q: What is the difference between the NFIP and private flood insurance?
A: The NFIP is a government-backed program that provides flood insurance to homeowners and businesses in participating communities. Private flood insurance is offered by private insurance companies.
- Coverage: Both NFIP and private flood insurance cover similar types of damage. However, private insurers may offer more flexible coverage options and higher coverage limits.
- Pricing: NFIP premiums are typically based on location and flood risk zone, while private insurers may use more risk-based pricing models.
- Availability: The NFIP is available nationwide, while private flood insurance may not be available in all areas.
Q: How do I get flood insurance?
A: You can purchase flood insurance through an insurance agent or broker. You can also purchase flood insurance directly from the NFIP website.
Q: How much does flood insurance cost?
A: The cost of flood insurance varies depending on several factors, including:
- Location: Premiums are higher in areas with a higher risk of flooding.
- Type of property: The type of building and its construction materials can affect the premium.
- Coverage amount: The amount of coverage you choose will determine the premium.
- Flood mitigation measures: Implementing flood mitigation strategies can qualify you for discounts on your premium.
Q: What are some tips for reducing my flood risk?
A: Here are some tips for reducing your flood risk:
- Elevate your home: Raising your home above the base flood elevation can significantly reduce your risk of flood damage.
- Install flood barriers: Flood barriers can help to protect your home from rising floodwaters.
- Improve drainage: Enhancing your drainage systems can prevent water from accumulating around your property.
- Be prepared: Have a flood preparedness plan in place, including an emergency kit and evacuation route.
Conclusion
The flood insurance market is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the increasing awareness of flood risk and the changing realities of climate change. As the frequency and severity of floods continue to rise, it is essential for homeowners to understand the evolving landscape of flood insurance coverage and to take steps to protect themselves from potential financial hardship.
By embracing the opportunities presented by technology, collaboration, and public awareness, the flood insurance market can evolve to meet the needs of a changing world.
Source:
- FEMA: https://www.fema.gov/
- NFIP: https://www.floodsmart.gov/
Closure
We hope this article has helped you understand everything about Riding the Waves of Change: A Deep Dive into Flood Insurance Coverage Trends. Stay tuned for more updates!
Make sure to follow us for more exciting news and reviews.
Feel free to share your experience with Riding the Waves of Change: A Deep Dive into Flood Insurance Coverage Trends in the comment section.
Keep visiting our website for the latest trends and reviews.
